- Published on
设计模式(15)——解释器 Interpreter
- Authors

- Name
- Leon
十五、Interpreter(解释器模式,类行为型模式)
1. 意图:
给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一个解释器,这个解释器使用该表示来解释语言中的句子。所谓的领域专用语言指的就是这种在某些领域使用的比较专业性的程序语言,为了实现这种语言,通常抽象一个解释器类去解析这种语言。
2. 适用:
当有一个语言需要解释执行,并且你可将该语言中的句子表示为一个抽象语法树时,可使用解释器模式。而当存在以下情况时该模式效果最好:
- 该文法简单对于复杂的文法,文法的类层次变得庞大而无法管理。此时语法分析程序生成器这样的工具是更好的选择。它们无需构建抽象语法树即可解释表达式,这样可以节省空间而且还可能节省时间。
- 效率不是一个关键问题最高效的解释器通常不是通过直接解释语法分析树实现的,而是首先将它们转换成另一种形式。
3. 类图:
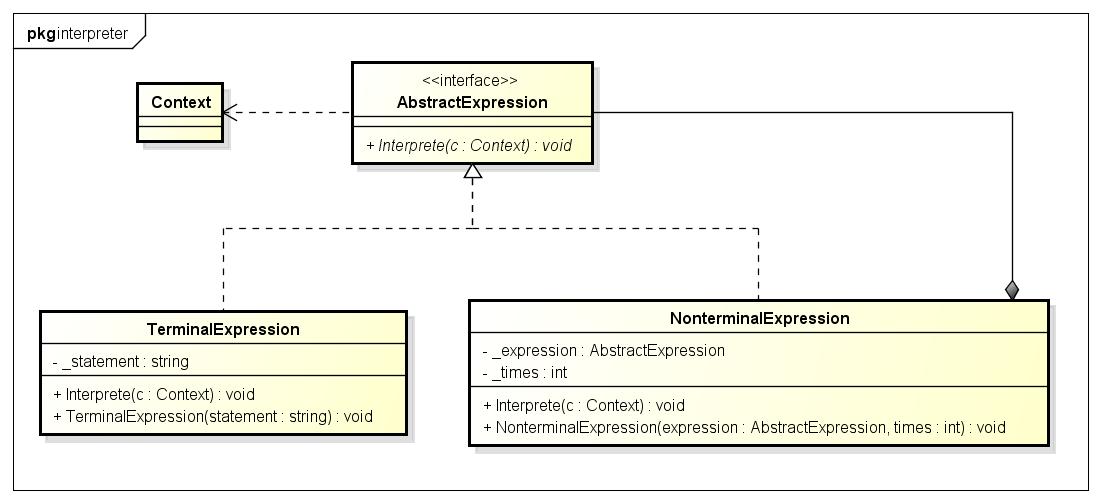
4. C++实现:
- 编写一个抽象基类
AbstractExpression,包含一个解释函数Interprete() - 编写一个实现类
NonterminalExpression(),has-aAbstractExpression 对象_expression - 编写实现类的
Interprete()方法,内部再调用_expression对象的Interprete()方法,实现递归调用,递归解释语法树。
Interpreter.h
//Interpreter.h
#pragma once
#include "Context.h"
#include <string>
using namespace::std;
class AbstractExpression {
public:
virtual ~AbstractExpression();
virtual void Interprete(const Context& c);
protected:
AbstractExpression();
private:
};
class TerminalExpression : public AbstractExpression {
public:
TerminalExpression(const string& statement);
~TerminalExpression();
void Interprete(const Context& c);
protected:
private:
string _statement;
};
class NonterminalExpression : public AbstractExpression {
public:
NonterminalExpression(AbstractExpression* expression, int times);
~NonterminalExpression();
void Interprete(const Context& c);
protected:
private:
AbstractExpression* _expression;
int _times;
};
Interpreter.cpp
//Interpreter.cpp
#include "Interpreter.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace::std;
AbstractExpression::AbstractExpression() {}
AbstractExpression::~AbstractExpression() {}
void AbstractExpression::Interprete(const Context& c) {}
TerminalExpression::TerminalExpression(const string& statement) {
this->_statement = statement;
}
TerminalExpression::~TerminalExpression() {}
void TerminalExpression::Interprete(const Context& c) {
cout << this->_statement << " TerminalExpression" << endl;
}
NonterminalExpression::NonterminalExpression(AbstractExpression* expression, int times) {
this->_expression = expression;
this->_times = times;
}
NonterminalExpression::~NonterminalExpression() {}
void NonterminalExpression::Interprete(const Context& c) {
for (int i = 0; i < _times; i++) {
this->_expression->Interprete(c);
}
}
Context.h
//Context.h
#pragma once
class Context {
public:
Context();
~Context();
protected:
private:
};
Context.cpp
//Context.cpp
#include "Context.h"
Context::Context() {}
Context::~Context() {}
main.cpp
//mina.cpp
#include "Context.h"
#include "Interpreter.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace::std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
Context* c = new Context();
AbstractExpression* te = new TerminalExpression("hello");
AbstractExpression* nte = new NonterminalExpression(te, 2);
nte->Interprete(*c);
return 0;
}